The first civilisations: Mesopotamia and Egypt
Agricultural and urban development
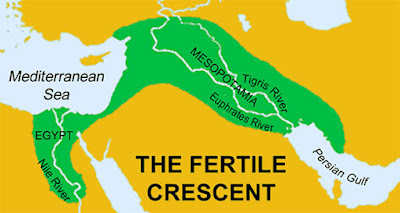
- The first great urban civilizations that developed their own writing system were born towards the 4th millennium BC on the banks of the Tigris and Euphrates rivers (Mesopotamia) and the Nile (Egypt).
- The control of water in the rivers allowed the growth of agricultural production, which favored commercial exchanges, the development of handicrafts and the birth of the first cities.
 |
| (From kickassfacts.com) |
- Independent city-states (Ur, Uruk...) emerged in Lower Mesopotamia etween 3500 an 2000 BC. They were ruled by kings
- Then, different dominant cities created empires in Mesopotamia:
- the Akkadian Empire
- the Kingdom of Ur
- the babilonian Empire
- The Assyrian Empire
- The ziggurat was the Mesopotamian temple. It was built with bricks and used the arch and the vault.
 |
| Amenophis IV. Cairo Museum |
The Egypt of the pharaohs
- The first monarchs or pharaohs considered themselves God's representatives on Earth and enjoyed of an absolute power (religious, political and military). To govern, they had the help of priests, officials and the army.
- The majority of the inhabitants of ancient Egypt were peasants and cultivated small portions of land. They gave a portion of the harvest to the officials of the king, pharaoh or temple (taxes).
- In the cities lived artisans, who worked in workshops under the orders of an official or priest, and traders. There were many servants, and the number of slaves was very small.
 |
| Vicens Vives |
 |
| Vicens Vives |
- The Egyptian religion was polytheistic, that is, it had numerous gods and goddesses that identified with the forces of nature.
- To worship the gods, numerous temples were erected, which were at the same time religious centers, economic and scientific. The temples represented the home of the gods and priests had to take care of them, worship them and offer them with offerings.
- The Egyptians believed in the existence of a life after death. To be able to access life from the afterlife the dead had to follow ritual: the mummification of the body and the Judgment of Osiris.
An art for eternity
- Funerary architecture had a great development in Egypt, with the mastabas, the pyramids and hypogea. The walls of these tombs are full of reliefs and paintings, which they show idealized scenes of daily life and representations of the gods.
 |
| Pyramids. Taken from Ingeoexpert |
- adobe: ladrillo de barro y paja sin cocer
- afterlife: vida después de la muerte
- artisan: artesano
- chamber: cámara (habitación)
- city-state: ciudad-estado
- crop: cultivo
- cuneiform: cuneiforme
- dynasty: dinastía
- flood: inundación
- hieroglyphic: jeroglífico
- mummufication: momificación
- irrigation: irrigación
- papyrus: papiro
- peasant: campesino, no posee sus tierras
- pharaoh: faraón
- polytheism: politeismo
- pyramid: pirámide
- priest: sacerdote
- sarcophagus: sarcófago
- scribe: escriba
- slave: esclavo
- riverbank: orilla de un río
- tax: impuesto
- tomb: tumba
- vault: vóbeda, cripta
- ziggurat: zigurat, templo escalonado
Documentary about Tutankhamun
Documentary about the pyramids




Comentarios